Starting from power generators to mobile drives, diesel engines are the most commonly utilized mechanical engines. They are widely used in a number of industries for a variety of purposes to complete.
Diesel engines are mechanical devices that work on the principle of internal combustion. In this method, the air inside is compacted and compressed to a high enough temperature in such a way that the diesel injected into the cylinder gets ignited. The combustion and the expansion are facilitated and actuated by a piston present in the assembly.
The purpose of a diesel engine is to convert the chemical energy extracted from the diesel fuel to mechanical energy. This transformation of energy is used for the production of power to the large scales of power-consuming units like the tractors, freight trucks, locomotives, and marine vessels, etc.
The idea of diesel engines is to make use of diesel combustion to produce energy. Let us understand the working procedure of diesel combustion fully to understand how diesel engines work.
 |
The Procedure of Diesel Combustion
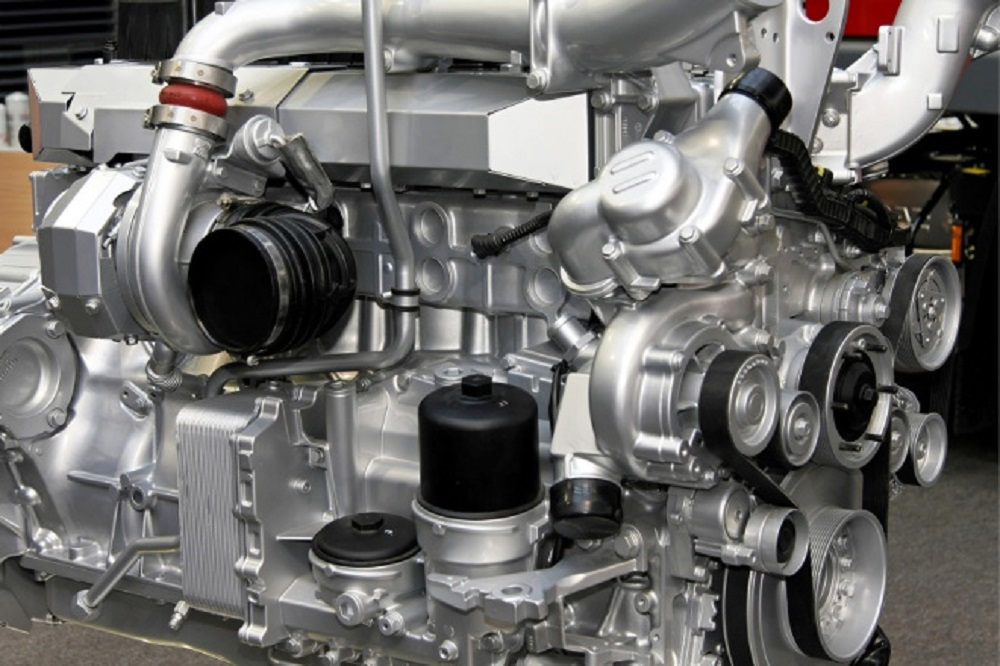
A diesel engine works on the functioning of diesel combustion. The diesel engine on its own is an alternating combustion device consisting of a piston and a cylinder. It can operate in two ways; two-stroke or four-stroke cycles, respectively. The diesel engine varies from the spark-ignition engine that runs on gasoline. The difference lies in the fact that the diesel engine injects air into the combustion chamber to create an impact on its intake stroke.
Both the two-stroke and four-stroke engines are designed with bores or cylindrical diameters less than 600mm or 24 inches in total. The diesel engines are designed in such a way that the combustion chamber has compression ratios of 14:1 and 22:1, respectively.
One must take note of the fact that engines with bores that are greater than 600mm are specifically two-stroke systems. The diesel engine functions by gaining energy through the combustion or the burning of the fuel injected into the system with compressed hot air present inside. The temperature of the air is taken to a degree such that it acts greater than the ignition temperature of the fuel that is injected into the system.
The air with a higher temperature than the ignition temperature of the fuel reacts instantaneously with the oxygen present in the air and burns to release energy. The additional heating of the cylinders often determines the air within the cylinder during the start-up of the engine. Two factors are used to assess the heat, these are the compression ratio and the operating temperature of the engine. Due to this mechanism, diesel engines are popularly known as the compression-ignition engines.
The correct control of the fuel injection is important to the performance of the diesel engine.
The Types of Diesel Engines
There Are Three Basic Types of Diesel Engines. They Are:
- Small
- Medium
- Large
The Features
- The categorization is based on their power capacities and outputs.
- The small engines have a power output of 188 kW. This is the most widely used diesel engine in the automotive industry.
- The medium engines have power ranging from 188 kW to 1006 kW. Most of them are used in heavy-duty trucks like freight trucks. The V-8 and V-12 engines belong to this group.
- The large engines have a power output above 750 kW. These are mostly used for the marine and locomotive industries. They are also used for electrical power generation.
- Apart from the sizes, there are also two-stroke and four-stroke engines in the market as well.
Concluding Thoughts
A diesel engine is a novel invention that has aided innumerable industries in the world and has helped industries and power tools to function with their new-age technologies honoring fool-proof science behind their functionalities.
Comments
Post a Comment